Fog Computing
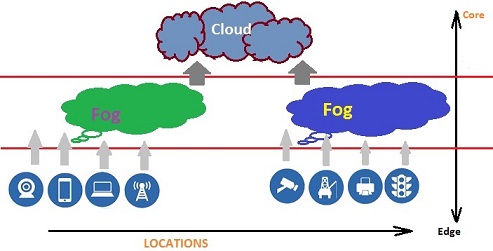
Fog computing also refer to Edge computing . Cisco Systems introduced the term “Fog Computing” and it’s not the replacement of cloud computing. Ideally cloud computing points to storing and accessing data and programs over the Internet instead of local computer’s hard drive or storage. The cloud is simply a metaphor for the Internet. In Fog computing, data, processing and applications are concentrated in devices at the network edge. Here devices communicate peer-to-peer so that data storage and share can be boosted to take local decisions. Smart devices can be effectively utilized to initiate Fog computing where data can be processed locally.
Fog Computing is a highly virtualization platform which is responsible to provides compute, storage, and networking services between end devices and traditional Cloud Computing Data Centers. Using Fog computing, we can conserve the network bandwidth, improve systems response time and security enhancement by keeping data close to the edge. Also reduce network and internet latency. Hardware and equipment are matter of concern to develop Fog computing. Besides authentication, privacy as well as wireless network security has to be analyzed precisely to avoid any data leak in Fog computing. Major benefits we can achieve on Fog computing are lower operational cost, quicker development as well as device independence. We can leverage Fog computing for heavy duty data crunching that enable better process and explore huge volume of data related to internet information. Internet of Things (IoT) concept has fully supported by Fog computing in which most of the devices used by humans on a daily basis will be connected to each other. As a examples, we can point to phones, wearable health monitoring devices, connected vehicle and augmented reality using devices such as the Google Glass.